TopoGEN scientists have created a novel, cell based kit to follow NHEJ by simply assaying for the presence of GFP positive cells (Fig 1).
DNA Repair pathways in animal cells can be divided into two main categories: HR and NHEJ. Homologous recombination (HR) is a minor pathway but very important in protecting cells from genotoxicity. NHEJ is the major repair pathway in all animal cells and operates continuously during the entire cell cycle. NHEJ is error-prone, but also pivotal in survival of cells since it is a re-ligation pathway that maintains genome integrity.
A specific reporter based assay for NHEJ can be very beneficial for anti-cancer drug discovery projects, learning more about the process of NHEJ repair and establishing intersecting pathways and druggable pathway targets.
The CN1.4 cell line is a clone derived from mouse embryonic day 13 neuronal cultures. The line was transformed using the temperature-sensitive SV-40 Large T-antigen The kit uses GFP as an in situ readout for NHEJ activity in a cell context.
DNA is continually being exposed to genotoxic agents leading to cell death and/or changes in gene expression. Of the various forms of DNA damage, the most dangerous are DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which may create serious problems arising from inappropriate recombination such as chromosomal translocations. To deal with the threats posed by DSBs, cells have developed multiple mechanisms to detect, signal, and repair the regions in chromatin. Two main pathways, HR and NHEJ, are involved in the repair of DSB. These pathways are further subdivided into more specific sub-pathway processes. In prokaryotes, HR has been known to be a major pathway for the repair of DSBs, while in eukaryotes, NHEJ was thought to be preferred. These pathways are largely distinct from one another and function in complementary ways. While NHEJ is not cell cycle dependent, HR is strongly S-phase dependent. NHEJ involves the ligation of two DNA ends without homology and tends to be error-prone while HR is high fidelity and essentially error free. In NHEJ, the broken DNA ends are modified for compatibility and then simply rejoined to restore DNA integrity. The resealing step is aided when there is some degree of micro-homology, even if only a few base pairs.
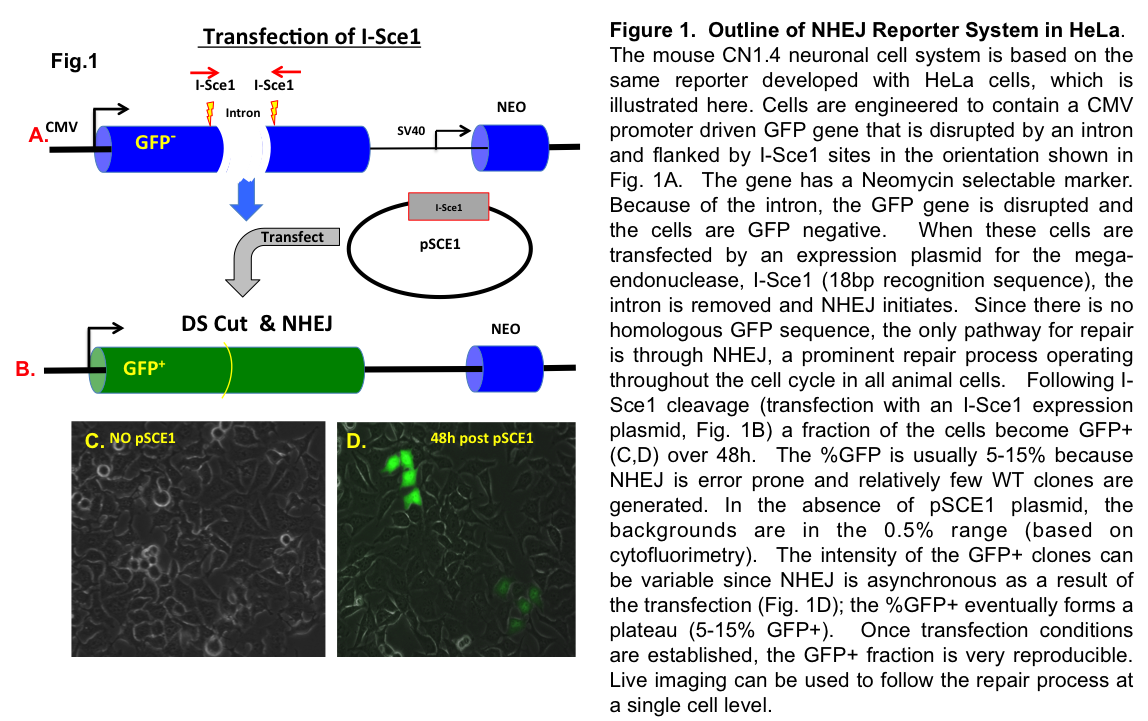
This mouse cell-based/cell context system has been designed to allow researchers to examine and interrogate the NHEJ process in neuronal lineage cells. The method relies on a mutated GFP reporter that has two I-Sce1 sites disrupting the gene. When I-Sce1 is transfected, the incompatible I-Sce1-cleaved ends are repaired by NHEJ and the cells become GFP positive (over a 2-4d window). These cells can be tracked by live imaging or assayed using Cytometry, Cytometry imaging tools or simply counting %GFP+ cells by fluorescence (see Fig. 1D).

